conductor, ℓ, with the resistance, R. The circuit is connected as shown in Diagram 1.1.
Seorang murid menjalankan eksperimen untuk mengkaji hubungan antara panjang suatu
konduktor, ℓ, dengan rintangan , R . Sambungan litar .ditunjukkan pada Rajah 1.1
The length of the
constantan wire between P and Q is adjusted so that its length,
ℓ = 20.0 cm. The switch is
on and the rheostat is adjusted until the current, I, flowing in the circuit is 0.2 A.
The potential difference, V,
across the wire is recorded.
Dawai konstantan dengan panjang, ℓ = 20.0 cm
diletakkan antara P dan Q . Suis
dihidupkan dan reostat dilaraskan sehingga arus elektrik , I, yang mengalir di
dalam litar adalah 0.2 A. Beza keupayaan merentasi dawai , V, di rekodkan.
The procedure is
repeated by varying the values of ℓ to be 30.0 cm, 40.0 cm, 50.0 cm and 60.0 cm. For each length of wire used, the rheostat is
adjusted so that the current is at a constant value of 0.2 A. The corresponding readings of the voltmeter
are shown in Diagram 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5 and 1.6.
Prosedur di ulang
dengan menggantikan panjang dawai konstantan, ℓ
dengan nilai
30.0 cm, 40.0 cm, 50 cm dan 60 cm. Untuk setiap panjang
dawai konstantan , reostat dilaraskan
supaya arus elektrik sentiasa mengalir pada nilai tetap 0.2 A. Bacaan-bacaan
yang sepadan bagi voltmeter adalah ditunjukkan pada Rajah 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5 dan 1.6.
(a)
Based on the aim
and the procedure of the experiment state the:
Berdasarkan tujuan dan prosedur eksperiment ini, nyatakan
(i) The manipulated variable
Pembolehubah yang dimanipulasikan
Length / L
[ 1 mark]
(ii) The
responding variable
Pembolehubah yang bergerakbalas
Resistance / R //
Potential difference / V
[ 1 mark]
(iii) The
constant variable
Pembolehubah yang dimalarkan
Diameter of the wire //
Cross-sectional area of the wire // Type of wire //current
(b)
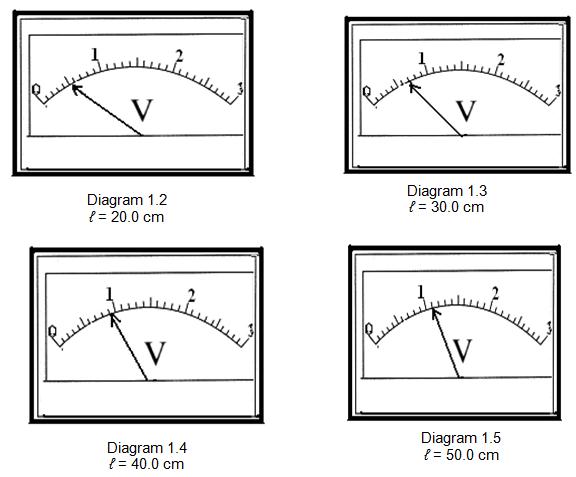
Record the reading of the voltmeter, V in Diagram 1.2, 1.3, 1.4, 1.5 and 1.6
when
different length of wires, l are
used. In each case, calculate the
resistance,
R of the wire where:
Rekodkan bacaan voltmeter dalam Rajah 1.2, 1.3, 1.4,
1.5 dan 1.6 pada bacaan panjang dawai
yang berbeza, ℓl yang digunakan. Pada setiap nilai tersebut hitungkan rintangan R dawai di
mana:
Tabulate your results for l, V,
I and R in the space below.
Jadualkan keputusan anda bagi ℓ, V, I dan R pada ruang di bawah.
|
L / cm
|
I / A
|
V / V
|
R / Ω
|
|
20.0
|
0.2
|
0.5
|
2.5
|
|
30.0
|
0.2
|
0.7
|
3.5
|
|
40.0
|
0.2
|
0.9
|
4.5
|
|
50.0
|
0.2
|
1.1
|
5.5
|
|
60.0
|
0.2
|
1.3
|
6.5
|
[6 marks]
(c)
On the graph paper on page 6,
plot a graph of R against ℓ.
Pada
kertas graf di halaman 6, plotkkan graf R melawan ℓ.
[5 marks]
Draw correctly a graph of R against L
(d)
Based on your graph, state the
relationship between R and ℓ.
Berdasarkan graf anda, nyatakan hubungan antara R dan ℓ.
Resistance is
directly proportional to length / R directly
proportional to L /
[1 mark]
(e)
State one precaution that should be taken to obtain the accurate readings
of V.
Nyatakan satu
langkah berjaga-jaga yang perlu diambil untuk mendapatkan bacaan
V
yang jitu.
Check the
voltmeter for zero error and make zero adjustment // Position of the eye such
that the image of the pointer in the mirror is blocked by the pointer to avoid
parallax error
[1
mark]
ANSWERS
Length
/ L
Resistance
/ R // Potential difference / V
Diameter of the wire //
Cross-sectional area of the wire // Type of wire //current
|
L / cm
|
I / A
|
V / V
|
R / Ω
|
|
20.0
|
0.2
|
0.5
|
2.5
|
|
30.0
|
0.2
|
0.7
|
3.5
|
|
40.0
|
0.2
|
0.9
|
4.5
|
|
50.0
|
0.2
|
1.1
|
5.5
|
|
60.0
|
0.2
|
1.3
|
6.5
|
Draw correctly a graph of R against L
Resistance is
directly proportional to length / R directly
proportional to L / 
Check the
voltmeter for zero error and make zero adjustment // Position of the eye such
that the image of the pointer in the mirror is blocked by the pointer to avoid
parallax error